What is a 4 axis press brake?
A 4 axis press brake is a machine tool that is used to bend sheet metal and plate. It consists of a stationary bed and a moveable ram, which is equipped with a punch that is used to apply pressure to the workpiece. The workpiece is held in place by a set of dies, which are mounted on the bed of the press brake.
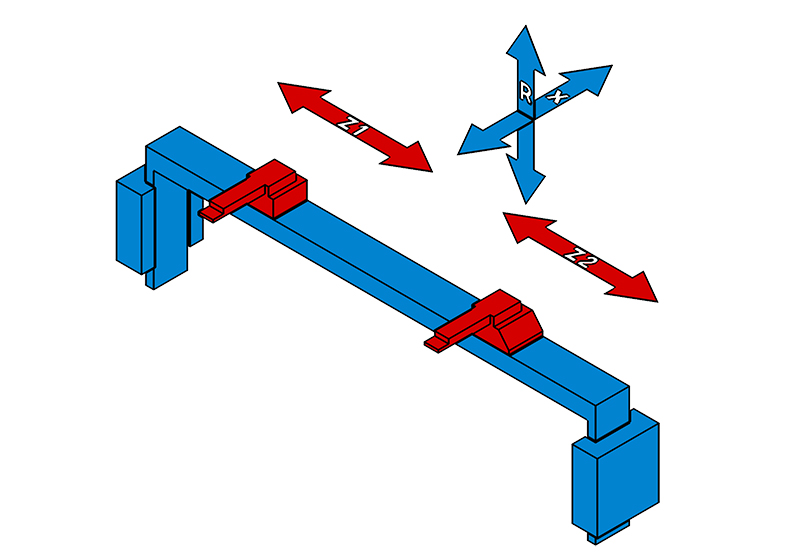
The traditional 2 axis press brake has two axes of motion: the X-axis, which is the left-to-right movement of the ram, and the Y-axis, which is the up-and-down movement of the bed. In a 4 axis press brake, there is an additional Y1-axis, which allows the bed to tilt left and right. This 4th axis (Y1-axis) can be used to create angled bends in the workpiece, which is not possible with a 2 axis press brake.
4 axis press brakes are used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, for tasks such as forming sheet metal parts, bending tubes and pipes, and creating custom shapes. They are typically more expensive and complex than 2 axis press brakes, but offer more flexibility and precision in the bending process.
What are the advantages of using a 4 axis press brake compared to a traditional 2 axis press brake?
There are several advantages to using a 4 axis press brake compared to a traditional 2 axis press brake:
Increased flexibility:
The 4th axis (Y1-axis) on a 4 axis press brake allows you to create angled bends in the workpiece, which is not possible with a 2 axis press brake. This can be particularly useful for creating custom shapes and for working with materials that are difficult to bend.
Improved accuracy:
The 4 axis press brake is generally more precise than a 2 axis press brake, which can be important for certain applications where high accuracy is required.
Reduced setup time:
With a 4 axis press brake, you can program the machine to perform multiple bends in a single setup, which can save time compared to setting up the machine for each bend individually.
Increased productivity:
The ability to perform multiple bends in a single setup can also increase the overall productivity of the machine, as you can complete more parts in a shorter amount of time.
Improved quality:
The increased accuracy and flexibility of a 4 axis press brake can lead to improved quality of the finished parts.
It's worth noting that 4 axis press brakes are typically more expensive and complex than 2 axis press brakes, and may not be necessary for all applications. It's important to carefully consider your needs and budget before deciding which type of press brake is right for you.
How does the 4th axis (the Y1-axis) on a 4 axis press brake work and what is it used for?
The 4th axis (Y1-axis) on a 4 axis press brake is a tilting axis that allows the bed of the press brake to tilt left and right. This is achieved by mounting the bed on a pivot point, which is controlled by a hydraulic cylinder or a servo motor.
The Y1-axis is used to create angled bends in the workpiece. This can be particularly useful for creating custom shapes and for working with materials that are difficult to bend. It can also be used to create multiple bends in a single setup, which can save time and increase productivity.
To use the Y1-axis on a 4 axis press brake, you need to program the machine with the desired angle of tilt. The angle can be entered manually or imported from a CAD drawing. The machine will then tilt the bed to the specified angle and perform the bend.
It's worth noting that the Y1-axis is only available on 4 axis press brakes, and is not present on 2 axis press brakes. If you need the ability to create angled bends in your workpieces, you will need to use a 4 axis press brake.
Can a 4 axis press brake perform all of the same tasks as a 2 axis press brake, or are there certain limitations?
A 4 axis press brake is generally capable of performing all of the same tasks as a 2 axis press brake, with the added ability to create angled bends in the workpiece using the Y1-axis. This makes the 4 axis press brake a more flexible and versatile machine than a 2 axis press brake.
However, there may be certain limitations to what a 4 axis press brake can do, depending on the specific model and its capabilities. Some 4 axis press brakes may not have the same tonnage or length as a 2 axis press brake, which could limit the size and thickness of the materials that can be bent. It's important to carefully consider the capabilities of the machine and ensure that it is suitable for your application.
In general, a 4 axis press brake is a good choice if you need the ability to create angled bends in your workpieces and/or if you require higher precision and accuracy in the bending process. However, if you only need to perform simple, straight bends, a 2 axis press brake may be sufficient.
How do you set up and program a 4 axis press brake?
Setting up and programming a 4 axis press brake can be a complex process, as it involves configuring the machine, setting up the workpiece, and entering the bending parameters into the machine's control system. Here is a general outline of the steps involved in setting up and programming a 4 axis press brake:
Prepare the machine:
Make sure the machine is clean and in good working order. Check that all safety guards and devices are in place and functioning properly.
Install the tooling:
Mount the punch and die on the ram and bed of the press brake, respectively. Make sure the tooling is properly aligned and tightened.
Set up the workpiece:
Place the workpiece on the bed of the press brake, making sure it is properly aligned and supported. Use clamps or other fixtures to hold the workpiece in place if necessary.
Enter the bending parameters:
Use the control system to input the desired bending angle, tonnage, and other parameters for the bend. If needed, import a CAD drawing or use the control system's programming interface to specify the bend line and other details.
Test the setup:
Perform a test bend to make sure the machine is set up correctly and the workpiece is being bent as desired. Make any necessary adjustments to the machine or the workpiece.
Begin production:
Once the setup is complete and the test bend is successful, you can begin production. Make sure to monitor the machine and the workpiece throughout the bending process to ensure that everything is running smoothly.
It's worth noting that the specific steps and procedures for setting up and programming a 4 axis press brake may vary depending on the specific machine and control system you are using. It's important to consult the machine's manual and/or seek guidance from the manufacturer or a qualified technician if you are uncertain about any aspect of the setup process.
What safety precautions should be taken when operating a 4 axis press brake?
There are several safety precautions that should be taken when operating a 4 axis press brake:
Wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE):
This may include safety glasses or goggles, gloves, hearing protection, and other appropriate clothing and equipment.
Follow all safety procedures and guidelines:
Make sure you are familiar with the machine's safety features and know how to use them properly. Follow all relevant safety procedures and guidelines, such as maintaining a safe distance from the machine while it is in operation, using proper lifting techniques, and avoiding loose clothing or jewelry that could get caught in the machine.
Keep the machine and work area clean and well-maintained:
Make sure the machine is clean and in good working order, and keep the work area free of clutter and debris.
Use caution when handling hot parts:
The punch and die of the press brake can become hot during the bending process. Use caution when handling hot parts, and use tongs or other appropriate tools to avoid burns.
Use caution when handling sharp edges:
The workpiece may have sharp edges after it has been bent. Use caution when handling the workpiece and use appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, to avoid cuts and abrasions.
Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures:
When performing maintenance or repairs on the machine, make sure to follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that the machine is properly isolated and de-energized before you begin working on it.
By following these safety precautions, you can help to prevent accidents and injuries while operating a 4 axis press brake. It's important to always be vigilant and take safety seriously when working with any type of machinery.
How do you troubleshoot and maintain a 4 axis press brake?
Here are some general steps you can follow to troubleshoot and maintain a 4 axis press brake:
Identify the problem:
Determine what is causing the issue with the machine. This may involve inspecting the machine for visible signs of damage or malfunction, as well as performing diagnostic tests using the machine's control system or other diagnostic tools.
Isolate the problem:
If possible, try to narrow down the problem to a specific component or system. This can help you to more effectively troubleshoot the issue and determine the most appropriate course of action.
Check for common problems:
There are certain issues that are more commonly encountered with press brakes, such as worn or damaged tooling, electrical problems, or hydraulic issues. Check for these common problems and see if they are the cause of the issue you are experiencing.
Consult the manual:
If you are unable to identify or fix the problem on your own, consult the machine's manual or seek guidance from the manufacturer or a qualified technician. They may be able to provide you with additional troubleshooting tips or assist you with diagnosing the issue.
To maintain a 4 axis press brake, it's important to follow a regular maintenance schedule and perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning and lubricating the machine, inspecting and replacing worn or damaged parts, and ensuring that all safety guards and devices are in good working order. It's also a good idea to keep accurate maintenance records, as this can help you to identify patterns or trends that may indicate a problem with the machine.
By regularly troubleshooting and maintaining your 4 axis press brake, you can help to extend its lifespan and ensure that it is operating at its best. This can help to improve the quality of your finished parts and increase the overall productivity of the machine.
What are the different types of 4 axis press brakes available on the market and how do you choose the right one for your application?
There are several different types of 4 axis press brakes available on the market, which can vary in terms of their size, capacity, features, and price. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a 4 axis press brake for your application:
Capacity:
Consider the size and thickness of the materials you will be working with, as well as the maximum tonnage and bending length that you will need. Make sure to choose a machine that is capable of handling your needs.
Precision:
If you require high levels of precision in your bends, you may want to look for a machine that is equipped with features such as a high-resolution CNC control system, laser or vision systems for aligning the workpiece, and advanced tooling options.
Speed:
If you need to produce parts quickly, you may want to look for a machine that is designed for high-speed production. This may involve features such as servo-driven axes, automatic tool changers, and other time-saving features.
Flexibility:
If you need to be able to perform a wide range of bending tasks, you may want to look for a machine that is highly flexible and versatile. This may involve features such as multiple tooling stations, a wide range of available tooling options, and the ability to program and store multiple bending programs.
Ease of use:
If you are new to press brake operation, you may want to look for a machine that is easy to set up and use. This may involve features such as a user-friendly control system and intuitive programming interface.
Budget:
Consider your budget and the overall cost of the machine, including the initial purchase price, ongoing maintenance costs, and any necessary tooling or accessories. Make sure to choose a machine that is within your budget and that provides good value for your investment.
By considering these factors and evaluating the different options available, you can help to ensure that you choose a 4 axis press brake that is well-suited for your application and meets your specific needs.










